
A 'smiley face' found on Mars could be the key to finding life on the Red Planet.
Last week, the European Space Agency (ESA) shared a picture of a 'smiley face' on the surface of Mars to Instagram.
The face, made up of two circles and a line inside a larger circle, can only be seen under infrared light and is thought to be the remnants of an ancient lake that dried up billions of years ago.
The image was taken by ESA's ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter, which has been recording the levels of methane and other gases in the planet's atmosphere since 2016.
Advert
A caption accompanying the smiley face reads: "Once a world of rivers, lakes, and possibly oceans, Mars now reveals its secrets through chloride salt deposits found by our ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter.
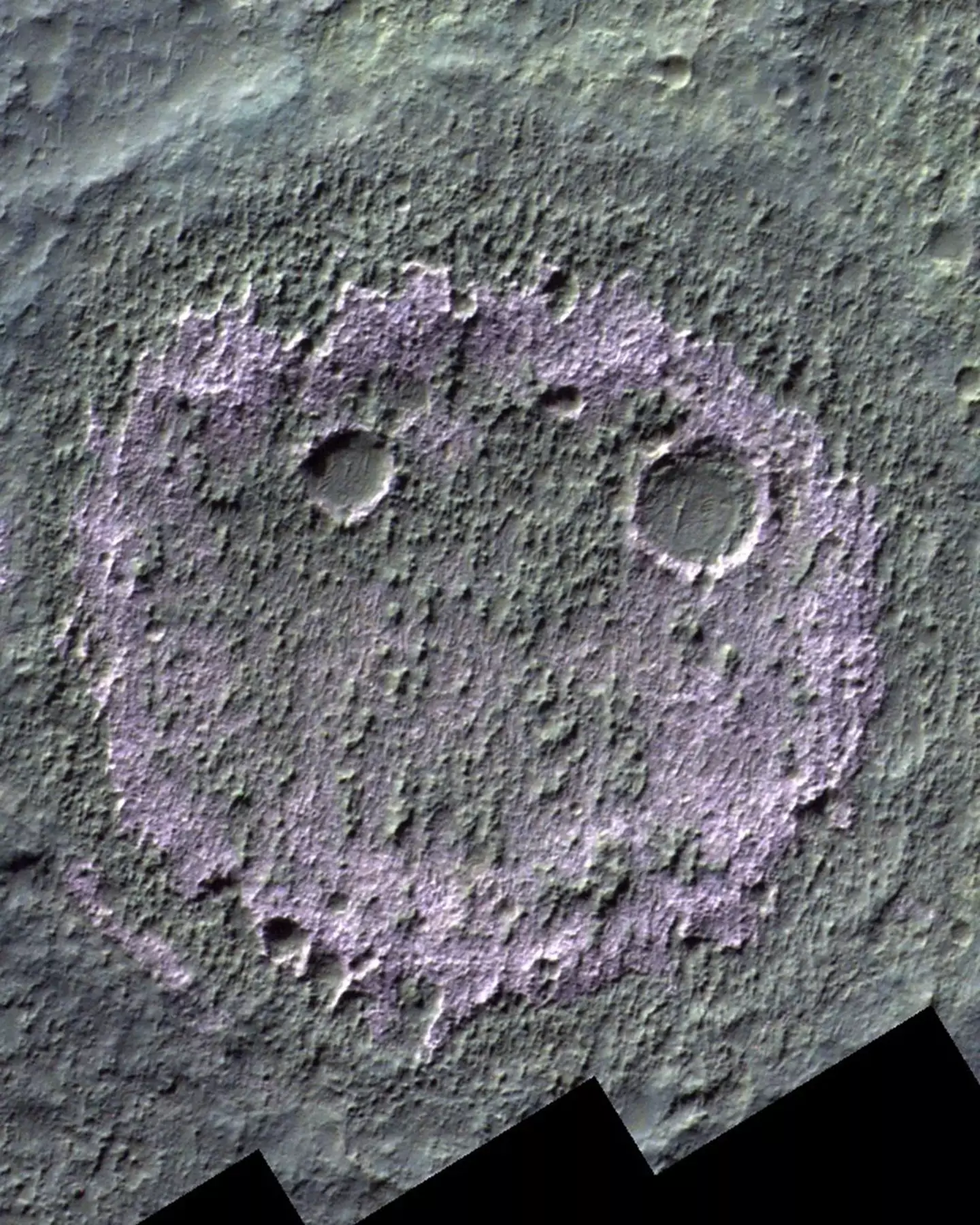
"These deposits, remnants of ancient water bodies, could indicate habitable zones from billions of years ago.
"The discovery of nearly a thousand potential sites offers new insights into Mars’ climate and potential for past life."
While Mars is currently a desert, billions of years ago, it was covered by rivers, lakes and potentially even oceans.
A research paper about ESA's discovery was published in the journal Scientific Data last month.
"In the distant past, water formed magnificent landforms such as riverbeds, channels, and deltas on the Red Planet," said planetary scientist and study lead author Valentin Bickel in a statement for ESA.
When these bodies of water disappeared over time, they left behind salt deposits like those that form the 'mouth' and outline of the face.
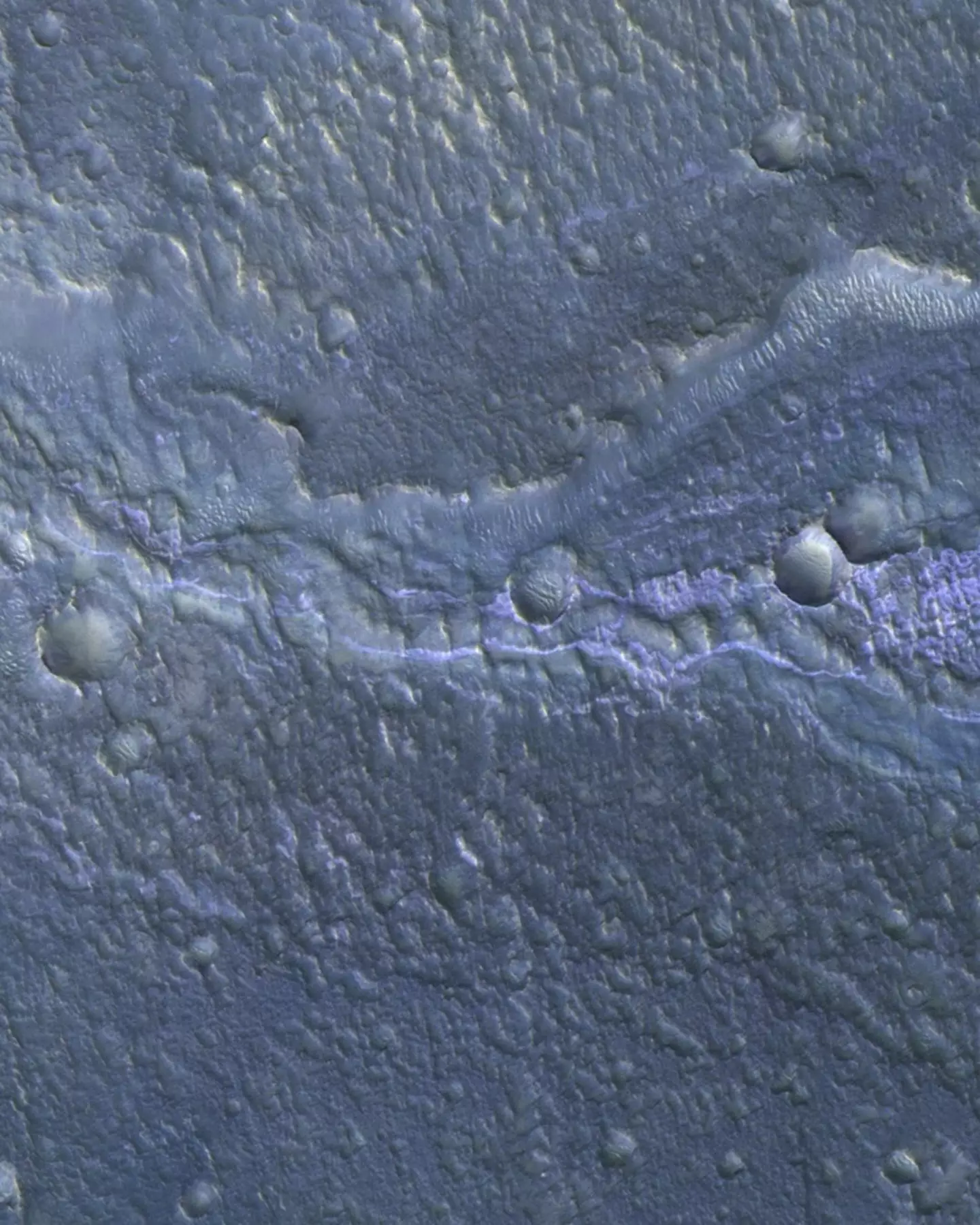
Deposits like these are important because they can 'provide optimal conditions for biological activity and preservation,' according to the study.
This makes them 'a prime target for astrobiological exploration,' researchers added.
In some locations, the leftover salts are the only evidence that water ever existed. As the water dried up, the high salt levels would have prevented it from freezing and been the last hope for any microscopic beings clinging onto life as Mars transformed to its current arid state.
If this is the case, the salts may have preserved vital evidence of these now-extinct lifeforms.
"The new data has important implications for our understanding of the distribution of water on early Mars, as well as its past climate and habitability," Bickel said.
So, while the discovery doesn't conclusively answer David Bowie's perennial question, it has reignited the search for life on the Red Planet.
